
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is a common condition encountered in orthopaedic practice. PFPS most commonly presents with retro- or peri-patellar pain associated with positions of the knee that result in increased or misdirected mechanical forces between the kneecap and femur. Climbing stairs, running, kneeling, squatting and long-sitting are frequent pain aggravators. Clinicians have come to understand that the cause of PFPS is not always directly at the knee, realizing the importance of surrounding dysfunctions proximal or distal to the site of pain….we must understand that knee pain is not about the knees (most of the time), a holistic approach must be utilized in both assessment and treatment to figure out why one would present with knee pain.
Here is a list of 4 common reasons for knee pain and a subsequent diagnosis of PFPS (which is a crappy diagnosis)
1) Weak Hips
You’ve probably heard it before, but it’s worth repeating: Weak hip abductor and external rotator strength is a key reason for PFPS. It is believed that weak hips cause medial rotation, adduction and valgus collapse of the tibia and femur leading to excessive joint compression and patellar mal-tracking. This is especially true in women due to the larger Q-angle they present with (wider hips), which makes it all the more important to strengthen the hips as part of a comprehensive treatment approach
“Current research reveals that poor proximal neuromuscular control and/or weakness of the hip musculature may lead to limited control of transverse and frontal plane motions of the hip (especially during single-legged stance). Other evidence suggests such dysfunction can result in dynamic malalignment including components of femoral adduction and internal rotation, valgus collapse at the knee, tibial rotation and foot pronation. Findings of deficits in hip abduction, extension and external rotation strength has also been shown with patients with PFPS. Further, multiple studies by Willson and colleagues demonstrate that there is an increased hip adduction angle in PFPS patients compared to healthy controls”
Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy 2012; 42(1): 22-29.
The Effects of Isolated Hip Abductor and External Rotator Muscle Strengthening on Pain, Health Status, and Hip Strength in Females with Patellofemoral Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial
American Journal of Sports Medicine 2011; 39(1): 154-163A Proximal Strengthening Program Improves Pain, Function and Biomechanics in Women with Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
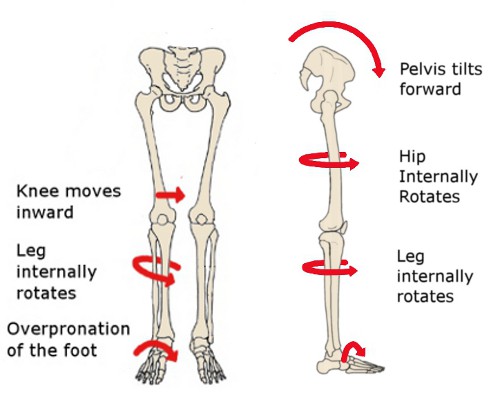
See what I’m talking about?
2) Restricted Ankle Dorsiflexion
I wrote an entire blog post about this a few weeks back. Long story short: If you can’t get the 10-15 degrees of dorsiflexion in your ankle that is needed for proper gait or squatting you will ultimately compensate by falling in on your arches thus pronating through your subtalor joint. Just like with weak hips, if you excessively pronate you will tend to have tibial and femoral internal rotation thus placing the knee in an awkward position when doing such tasks as descending stairs. Muscle imbalances my result along with excessive joint compression at the knee causing PFPS symptoms.
I have not come across a lot of studies that specifically look at the effects of ankle dorsiflexion on knee pain but here is what I’ve read to date:
N Am J Sports Phys Ther. 2009 February; 4(1): 21–28
Treatment of Lateral Knee Pain by Addressing Tibiofibular Hypomobility in a Recreational Runner
J Sports Rehab 2012 May;21(2):144-50.
Effect of limiting ankle-dorsiflexion range of motion on lower extremity kinematics and muscle-activation patterns during a squat.
“Altering ankle-dorsiflexion starting position during a double-leg squat resulted in increased knee valgus and medial knee displacement as well as decreased quadriceps activation and increased soleus activation. These changes are similar to those seen in people with PFPS.”

Knee to wall test: How I assess ankle doriflexion
3) Lumbar spine pathology:
Conditions like spinal stenosis, arthritis or a disc herniation from L3-4 (most likely) can refer pain down to the knee. The nerves that exit the lumbar spine at certain levels travel down to the knee to provide motor input and sensory output. Thus, irritation of a nerve root in the lumbar spine can be a chief cause of lateral (L5), anterior (L4) or medial (L3) knee pain. Anecdotally, I have treated a few clients with no back or upper leg pain, but complained of tightness and burning at the knee. Once all knee-specific subjective and objective tests are ruled out, it became apparent via dural mobility testing that the knee pain was a function of a lumbar spine pathology.
Quick tip: If a client has unexplained knee pain and you think it maybe neurologically mediated (well, all pain is neurologically mediated…you get what I’m saying though) then test dural mobility and see if that recreates their knee pain. If so, you have a great outcome measure to see if you made a difference post treatment. If a slump test causes burning lateral knee pain, treat the lumbar spine and re-test the slump. Hopefully it’s better afterwards!

4) Hallux Valgus or 1st MTP restriction:
Just like at the ankle, if the 1st toe can’t extend or dorsiflex like it should the foot will fall into more pronation through midstance to toe off (the big toe has to find a way to get to the ground and it does so by forcing the subtalor joint into pronation). This again leads to dynamic knee valgus and the possibility of PFPS…Knee pain? Check the big toe!

Good ROM
Summary:
- Knee pain is often multifactorial and keeping in mind regional interdependence yields a more comprehensive assessment and treatment approach
- Knee pain can have components of articular restriction, dural irritation, tendonopathy or a combination of many things (usually the case)
- When someone comes in with insidious onset unilateral knee pain and the prescription from their G.P says “overuse injury, treat with ROM, strengthening and stretching of the knee” (what I had last week) you MUST explain to the patient that unilateral overuse with bilateral activity (running etc) is probably impossible.
- Treat the joints above and below and even on the contralateral side if needed